What the heck is Google doing with visual search? More importantly, how can it help businesses and the marketers who market them?
That was the topic of a recent Grade.us and GatherUp co-sponsored webinar hosted by our own Garrett Sussman, as well as Mike Blumenthal of our sister company, GatherUp, along with David Mihm of Demand Science.
The webinar was packed with actionable insights, along with a few interesting predictions for what we can expect in the near future.
Catch it here:
Don’t have 48 minutes and change to watch? Here’s the recap of the most important points.
On the nature of visual search
Google seems to be replacing or subsuming text results in favor of image results. For example, Mihm noted image carousels have been popping up in place of 3-pack results.
There have also been instances where images augment the basic name, address, and phone number review data showing up in the traditional three pack.
Google has developed an incredible ability to look at an image, parse the elements of the image, and then understand what’s in the image.
On the nature of entities
These image results play into Google’s move to the development of entities. Blumenthal explained what this really means: they are people, places, and things. Essentially entities are layers of real world objects that Google creates relationships between and accumulates information about.
Local served as the test scenario for developing these objects, but entities have expanded to politicians, movies, movie actors, and more.
In local, though, entities are all about the places, the businesses, the people who own them, and the things they sell. On mobile in particular, Google is becoming a visual discovery environment, and it’s using entities to do it.
On what users are providing vs. what businesses provide
Google’s getting data from just about every source. Blumenthal noted there are thousands of edits and additions to Google Maps every day. Images come from:
- Business owners
- Users
- Scraping websites
- Local Guides
Blumenthal did note that business owners are now adding more content than at any time in the past, and stressed that business owners need to take control.
“Otherwise, their business listing at Google becomes a playground for consumers, which I think is a formula for disaster.”
Mihm notes that ThriveHive got some data in November of 2019. They were tracking the number of impressions on customer-added photos vs. business-added photos. Last year Google did announce they would give more preference to business-owner photos. If businesses are adding really granular photos on a regular basis then Google will start showing these business-owner photos in image-oriented carousels and packs.
On how businesses are taking advantage of visual opportunities
Mimh notes that GMB has become a lot more obvious in everyone’s searching experiences, and as such business owners have a vague sense of the Knowledge Panel.
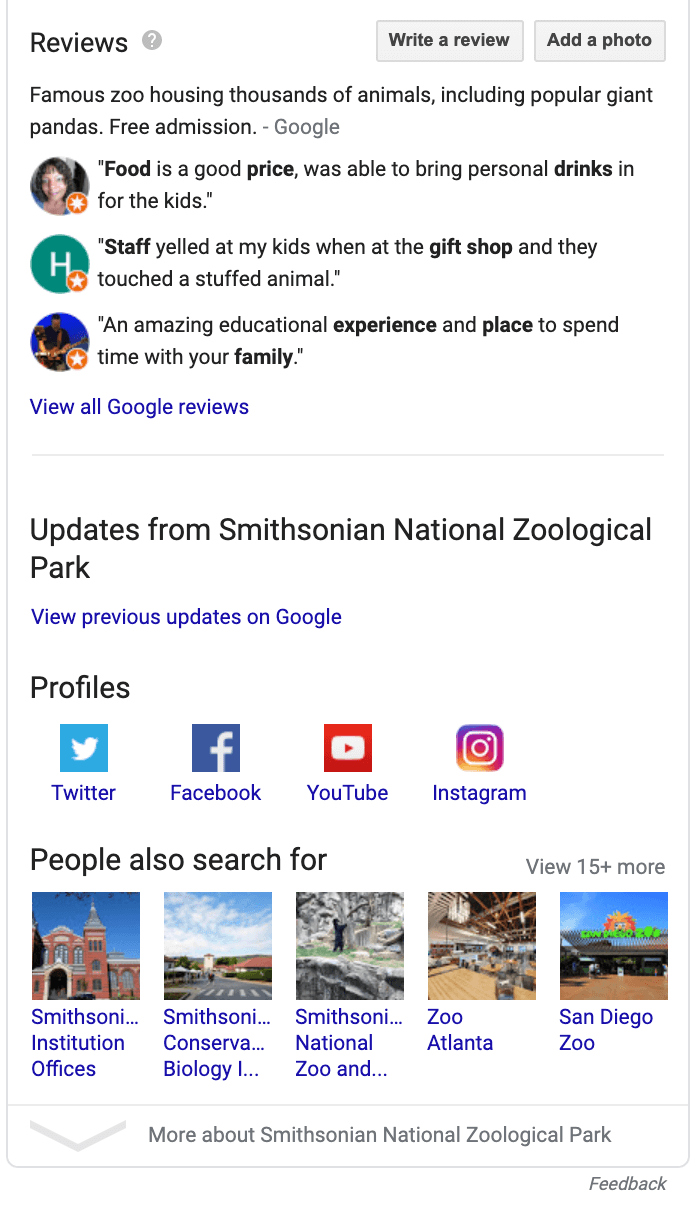
He also notes many people are still stuck in the traditional mindset of traditional business listings, in which they set their basic info and forget it.
Blumenthal added that many people are still doing their citations exactly the same way they did ten years ago. He stresses there are a broad range of new features, many of which revolve around these visual elements.
Businesses could really seize a competitive edge by adopting these visual elements now, because many businesses aren’t doing it.
Blumenthal provided an example of a client of his who runs a custom jewelry store. This individual is benefiting a great deal from being an early adopter of these features. Her store is on the third level of an office building. She has no street-level presence. She was able to boost her business by taking her own photographs and using them in Google posts.
Now, she comes right up when someone searches “engagement rings in Buffalo.”
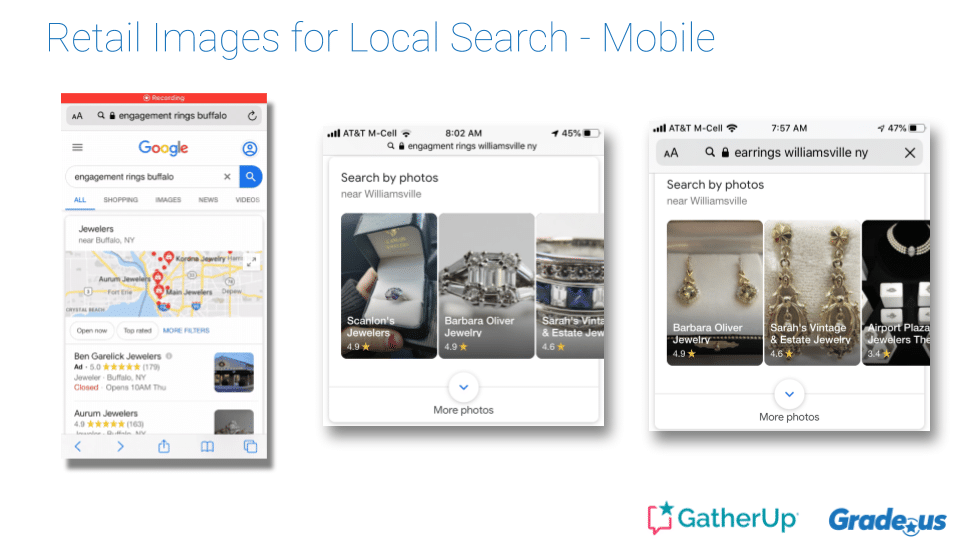
Google knows when it’s looking at engagement rings, earrings, and the rest of her stock. Google shows them in the search results, adds thumbnail images to her local pack, and is adding these images to anywhere else people are likely to do a product search.
On managing images: Retail, restaurant, and hotels
Service businesses can get a lot of mileage out of photographing staff members and placing those in their profile. If you can do a semantic image, like a photograph of a lawyer in the courtroom, so much the better. Home services can take photos of their guys doing the actual work.
Blumenthal says it’s important to stretch your imagination a little bit!
“Find an image that shows that person in the right place. It’s not always easy, but it’s almost always possible.”
On finding the right photographer
Using stock photos is a terrible idea, because Google can tell when an image has been used in 5,000 other places. It’s smart for business owners to either get good at photography or to hire photographers themselves.
Photos don’t just help convert. Blumenthal notes we have clear, present evidence that Google understands the entities in the images and so you’re using them to edify Google and what Google understands about your business.
Your images won’t necessarily change your rank in Google, but they can do things like fixing your street view. Street views go out of date and it can be confusing to customers when they do. They can also do 360 degree tours of the interior of your building.
On Google image analysis and getting images approved
Google does flag a lot of images as being inappropriate even when they’re not, such as Yoga photos, massage photos, and even photos of physical therapists working on a leg. It has a lot to do with the legal standards and Google’s advertising policies.
You can use the Vision AI Tool at cloud.google.com/vision to discover which of your photos will get approved and why or why not. Sometimes tricks like switching a photo to black and white can reduce Google’s sense that it’s “racy” or inappropriate.
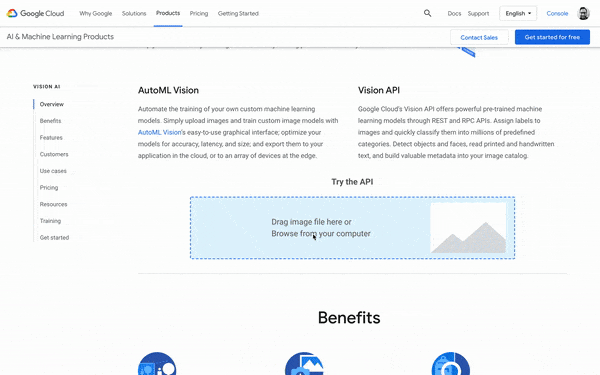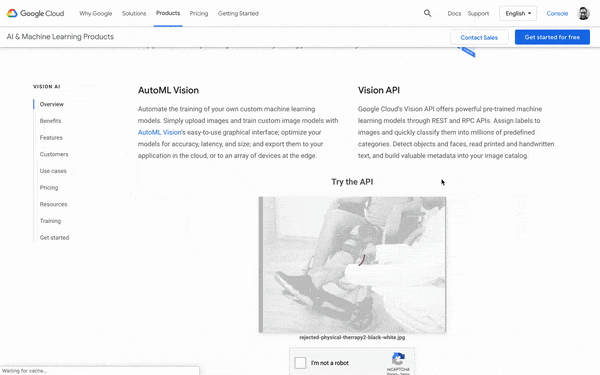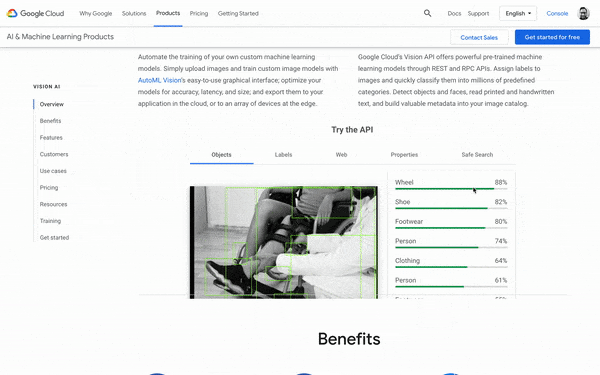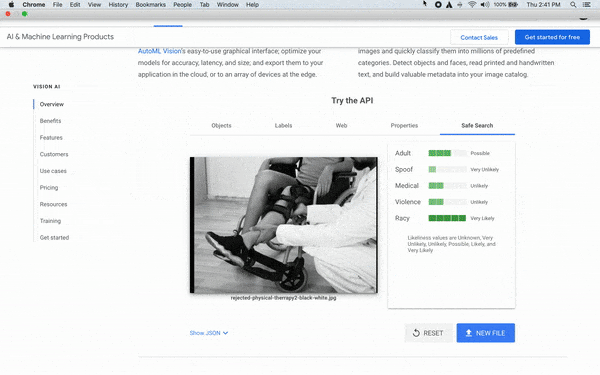
Visual search webinar takeaways
1. When Google presents an image-oriented pack or result, they’re either going to fill the void by not showing you as often or by using customer photos instead.
2. Images don’t necessarily drive your position in the SERPS, but they do offer a conversion optimization function, do give you more opportunities to be shown in searches, and do help Google understand your business better.
3. Your best bet is to take quality photos, even if it means hiring a photographer, and to release them over time. You also want to control them every place you can, including on places like Yelp, Facebook, and TripAdvisor.
4. It’s important to have photos on your own website. Remember, a high-quality site is about quality images and quality content.
5. Use the Vision AI tool to check your images before uploading them. This will help you avoid headaches and lose your Google post photos to the Nanny-bot.
Catch Mike Blumenthal at [email protected] or follow him on Twitter at @mblumenthal. You can catch David Mihm at [email protected] or at @davidmihm.









